Trading Partner Portal: Bolivia
Overview
Paraguay and Bolivia sign key cooperation agreements
Merco Press, June 13, 2024
Bolivia is the latest South American nation to use China’s yuan for trade in challenge to the dollar
Associated Press, July 27, 2024
Trade Overview
Bolivia is a central-South American country, bordered by Brazil, Argentina, Peru, Chile, and Paraguay, and is only one of two South American landlocked countries. Roughly one-third of the country is in the Andes Mountain range, and it also hosts a variety of different climates. It is rich in minerals including zinc, lithium, silver, and tin, with its lithium deposits being largely untouched. Its agricultural sector is growing quickly, and an important part of its growing economy.
With a population of just over 12 million people, Bolivia has a GDP of $48 billion. Bolivia is the second poorest country in South America; however, it has the had the fastest growing economy in terms of GDP. Main economic and exporting centers in Bolivia would be in the large cities of Santa Cruz, La Paz, El Alto, and Cochabamba, with a large part of the population living in these cities and much of its international business being conducted in these places. Bolivia has trade agreements with its neighbors and trades with a variety of other countries.
Bolivia – U.S Trade
As of 2024, U.S exports to Bolivia totaled $403 million, ranking 108th, with their top exports being petroleum and coal products ($97 million), computers and electronic products ($70 million), transportation equipment ($67 million), non- electrical machinery ($61 million), and chemicals ($46 million).
U.S imports from Bolivia totaled $503 million and Bolivia ranked 97th in U.S import markets. The top five imports being primary metals manufactures ($270 million), agricultural products ($84 million), minerals and ores ($38 million), processed foods ($19 million), and waste and scrap ($18 million).
California – Bolivia Trade
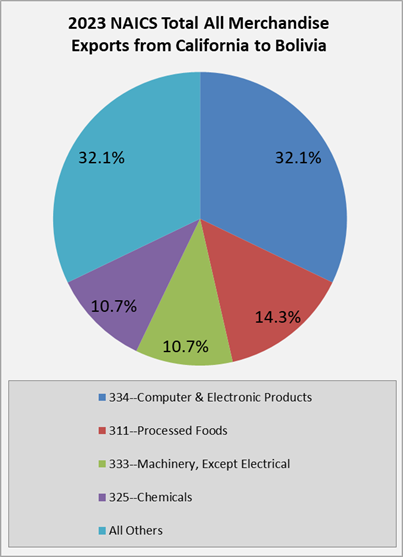
In 2024, California exported $20 million to Bolivia, with top exports being processed foods ($5 million), computer and electronic products ($4 million), chemicals ($4 million), transportation equipment ($2 million), and non-electric machinery ($2 million).
California imported a total of $33 million in products to Bolivia, with top imports being agricultural products ($42 million), primary metals manufactures ($8 million), wood products ($2 million), computer and electronic products ($2 million), and processed foods ($1 million).
FDI- Bolivia
In 2024, U.S FDI entering Bolivia totaled at $172 million, while $20 million was invested from Bolivia into the United States. Leading sectors for U.S exports and investments were energy, equipment and machinery, automobiles, healthcare, and agriculture. (International Trade Administration)
Bolivia and the World
Bolivia is ranked 62nd among world exporters, with total exports to the world equaling $9.06 billion. Total imports from the world to Bolivia were $9.90 billion, and Bolivia was ranked 69th in world importers. Bolivia is still considered an emerging market, with its purchasing power growing steadily. It is open to foreign direct investment with its partners, but there can be barriers for those looking to do business with Bolivia. Its non-renewable natural resources are one of its strong market qualities that has many countries trading with them, especially with the U.S. Likewise, U.S. products are seen as quality products in Bolivia, and the demand for them is increasing. Bolivia holds trade agreements and affiliations with its neighboring Latin American countries and the world; it continues to trade with other countries as well.
Trade Agreements
Trade Agreements
Trade Agreements and Issues
Bolivia is affiliated with the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), Andean Community (CAN), MERCOSUR, and WTO. It also has complimentary agreements with Chile (ACE 22), Panama, Cuba, and Mexico (ACE). These agreements eliminate tariffs and most trade barriers with the affiliated countries. Bolivia in the past was allowed duty free access or reduced duty rates under the General System of Preferences (GSP) for it is exports to the EU, Switzerland, Canada, Russia, Australia, U.S and others. GSP expired in 2020. It currently does not have a free trade agreement with the U.S.
The Bolivian government enforces a state centered economic plan, which makes it challenging to do international business for many countries and firms. The country also faces political instability, as well as conflicts within its main political party MAS (Movement Towards Socialism). Economic instability attributes primarily to its growing fiscal deficit, which is primarily derived from fuel import subsidies, and overspending. Lack of judicial help, corruption, and mirky investment incentives also make it difficult for foreign direct investment.
Events
Events